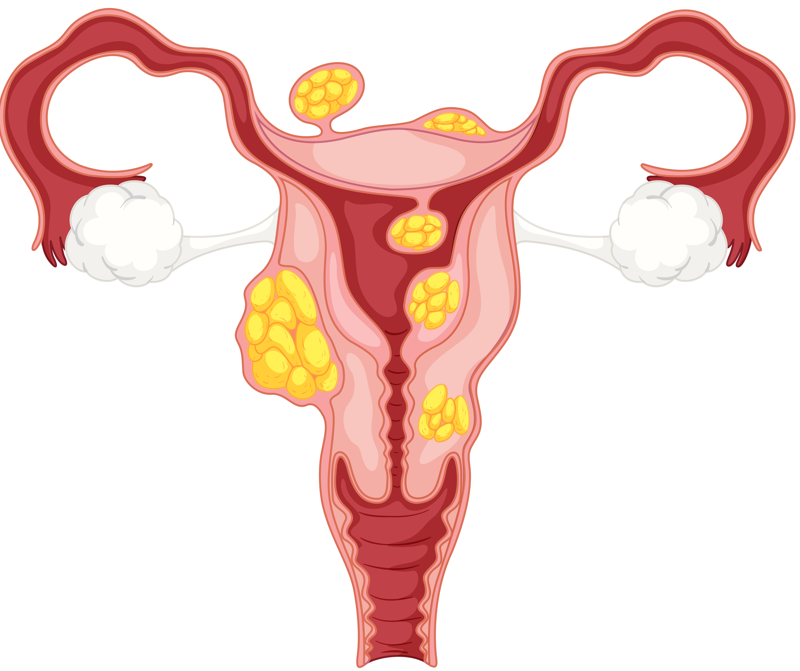
These growths occur in up to 50% of all women at some stage in their lives, usually during the reproductive years, and are one leading cause of hysterectomy (removal of the uterus). Medications and newer, less invasive surgical treatments are now available to help control the growth of fibroids.
What Causes Uterine Fibroids?
The exact reasons why some women develop fibroids are unknown but here are several factors that may influence their formation.
Family history. Fibroids tend to run in families, and affected women often have a family history of fibroids.
Women of African descent are two to three times more likely to develop fibroids than women of other races.
Hormones. Fibroids grow in response to stimulation by the hormone estrogen, produced naturally in the body by the ovaries. These growths can show up as early as age 20 but tend to shrink after menopause when the body stops producing large amounts of estrogen.
Pregnancy. Fibroids may develop and grow rapidly while you’re pregnant. This is because during pregnancy your body increases the production of estrogen and progesterone.
Fibroids can be tiny and cause no problems, or they also can grow to weigh several pounds. Fibroids generally tend to grow slowly.
Risk Factors of Uterine Fibroids
Risk factors that may likely cause you to have uterine fibroids include:
· Age; age of 30 or older
· Race; African heritage (occurring 3-9 times more often than in Caucasian women)
· Getting your period at a young age
· Being overweight.
· Birth control use
· Pregnancy
· Family history of fibroids.
What Are the Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids?
Most fibroids, even large ones, produce no symptoms. These masses are often found during a regular pelvic examination.
Symptoms of fibroids may include:
· heavy bleeding between or during your periods that includes blood clots
· pain in the pelvis or lower back
· increased menstrual cramping
· increased urination
· pain during intercourse
· menstruation that lasts longer than usual
· pressure or fullness in your lower abdomen
· swelling or enlargement of the abdomen
Treatment options for uterine fibroids.
Treatment for fibroids depends on the symptoms, the size and location of the fibroids, age (how close the person is to menopause), the patient’s desire to have children, and the patient’s general health.
Myomectomy is the surgical removal of the fibroids only. This can be accomplished through traditional surgery (involving an open cut), key-hole surgery, and hysteroscopy resection (involving a telescope in the vagina and uterus). The surgical approach depends on the size and location of the fibroid. Myomectomy can be performed for certain types of fibroids and preserves the potential for childbearing.
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus (and fibroids). It is the most commonly performed surgical procedure in the treatment of fibroids and is considered a cure. Depending on the size of the fibroid, hysterectomy can be performed with incisions through the vagina or abdomen. In some cases, the procedure may be performed using laparoscopy.
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) is a non-surgical treatment or clotting of the arterial blood supply to the fibroid. Blocking blood flow to the fibroid shrinks it. This method may prove to be a good option for women if other methods have not worked, she does not want surgery, or may not be good candidates for surgery.

Recent Comments